General Hospital in Mollet del Vallès
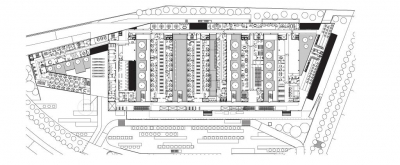
This new hospital serves some 150,000 persons, including the inhabitants of the city of Mollet del Vallès as well as those of other communities in the province of Vallès Oriental. Located on the ring road that surrounds the city, the site faces the neighbourhood of Can Borrell on one side and a large park on the other. Given the building s considerable dimensions (26,000 m²), one of the fundamental ideas behind the design was to control its size, both in relation to its urban and natural surroundings as well as in terms of the human scale. This concern is reflected in three outstanding characteristics.First of all, by taking advantage of the pronounced slope of the site, the project was approached as a predominately horizontal structure with volumes that unfold over the terrain in a staggered sequence as a way by which to reduce the visual impact of the building. Secondly, the volumes are organised around interior garden
patios, which provide light and ventilation. The identity of the patios for the hospital personnel, patients and visitors is established by the specific types of autochthonous trees and vegetation that are planted in each one.
Finally, a large public plaza has been placed at the main entrance of the hospital where a huge, ancient oak tree has been conserved. The plaza is a fundamental element of the
design in that it penetrates inside the hospital, where it is integrated into a circulation space that recalls a rambla - the traditional pedestrian promenade that characterises
Catalan cities - acting as a link between the city and building s interior.
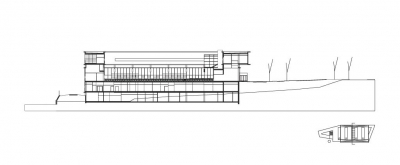
The facade that runs in the north-south direction starts as a one-floor volume on the south end and then increases in height to a two-storey volume all along the length of the
building to accommodate the inpatients area. In cross section, the building has a two-storey height on the western side and a three-storey height on the eastern side.
The predominant materials are reinforced concrete and glass. The facades are composed of ventilated polymer concrete panels and curtain walls of thermal glass. The floors are
marble and terrazzo. The partitions and false ceilings are plasterboard.
Sustainability
With respect to sustainability, three fundamental aspects were addressed:
1. Materials that ventilate and insulate
The use of a ventilated facade and materials to insulate both the facade and the roof contribute to the reduction of energy demands.
2. Exploitation of natural resources: geothermal, solar and photovoltaic energy
The use of these resources along with abundant natural light entering through the interior patios and the skylights significantly reduces the need for electricity.
3. Equipment that provides energy: efficient, low power and high performance The mixed system includes ceiling and floor heating and complementary air conditioning where needed.
The implementation of these measures in terms of the design as well as the technology utilized for its construction and maintenance makes the new hospital an example of sustainability for Catalan public architecture.







 copy.jpg)