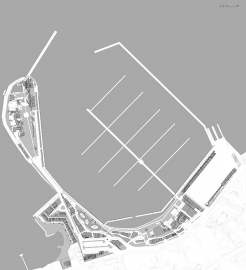
Yalikavak Palmarina
Yal?kavak is one of the lagoons on the southwestern coast of Turkey, which is becoming a popular destination for blue voyages along the Turkish Riviera.
Unlike its provincial center Bodrum, which has faced a building boom in 1980s with the increase of touristic activities, Yalikavak is still among relatively calm, silent and untouched bays of the peninsula.
The project for the renewal and extension of the existing marina complex, for the use of upper middle class in Yalikavak, has the burden of welcoming a big investment in this particular area, which consequently would also bring its own facilities. The main motivation of the design aimed both to correspond fully to the needs and desire of the new comers and to create a dialogue with the authentic qualities of the place, that would find its belongingness in the built and social aura of Yalikavak. This tendency may briefly be described as "being Mediterranean."
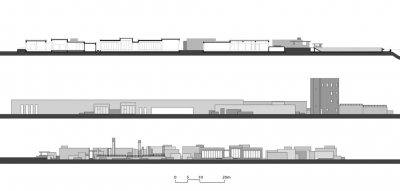
The complex was developed in three stages, constructed in consecutive years. Firstly the so called "island," that was connected to the mainland by a narrow passageway, to include mainly restaurants, the pool-beach club and some retail units. The programme also included sanitary and technical rooms needed for the mega-yachts that will dock at this part of the marina. Instead of a generic design that can easily become an alienated object for this place, an architecture derived from the local character, interpreted as a composition of masses with different heights, merging with the landscape and with the sea has emerged as a way to be integrated with Yalikavak, as a Mediterranean settlement. Alongside the masses that follows a grid structure in plan, atypical additions such as a linear wall and a tower accompanies the complex. Following the ancient cities like Kos, Rhodes and Siena that are fully cladded with a single material, travertine is used to render the whole complex which regards itself as a new-comer, but one of a familiar; not a hard-shell foreigner.
This design approach was followed in the consecutive stages this time with wide overhangs creating a continuous shaded path that sometimes turns into a colonnade alongside the public circulation path. These stages are mainly composed of various shopping and recreational units, including a small boutique hotel and some offices. Sanitary, technical and storage rooms of the marina were again dispersed. Various rows of shopping units are united by series of overlapping overhangs on different levels. Above all, the intensive use of the complex by all levels of the society was given priority, which mainly conflicts with worldwide acceptance of such marinas, to be so called elitist spaces with limited access. At Palmarina, architecture-management conformity succeeded in vast amount of public use just adjacent to the exclusive marine world.
The technical design of the complex was to be adapted at least to the Blue Flag marine codes, which foresees many sustainability issues like recycling the waste disposal not only from the buildings, but also from the yachts. Moreover, the use of architectural elements such as green roof and large overhangs provides excessive gain in cooling energy and adds to user comfort, at this summer-time complex.
Site: 104.000 m²
Building: 14.000 m²