85 Social Housing Units in Cornellà
85 dwellings, 543 spaces and 2172 corners
For the 10,000 m2 of built surface area of the new building in Cornellà de Llobregat (Barcelona), consisting of 85 social housing units laid out on five levels, a total of 8,300 m2 of zero kilometre timber from the Basque Country has been used.
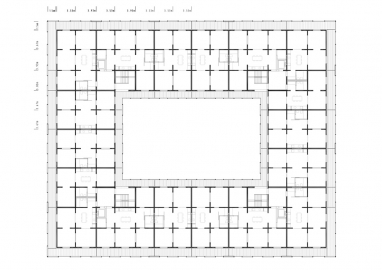
The bases of this new residential building are a matrix of communicating rooms that eliminates corridors to guarantee optimum use of the floor plan and the use of timber to enable the industrialization of elements, improved quality of construction and a major reduction of deadlines and C02 emissions.
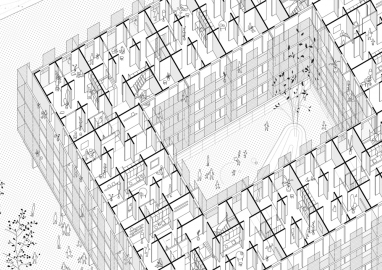
The building is organized around a courtyard that articulates a sequence of intermediate spaces. On the ground floor, a porch opens up to the city, anticipating the doorway of the building and filtering the relationship between public space and the courtyard that acts as a small plaza for the community. The four vertical communication shafts are situated at the four corners of the courtyard so that all the occupants converge and meet in the plaza, which represents a safe space from a gender perspective. On the model floor, entry to the apartments is from the communication shaft and the private terraces that make up the ring of outdoor spaces that overlook the courtyard. The building’s general floor plan is a matrix of communicating rooms. There are 114 spaces per floor, all of similar dimensions, eliminating both private and community corridors to make the maximum use of the floor space. The server spaces are laid out in the central ring, while the rest of the rooms, of undifferentiated use and size (13 m2), in the façade, accommodate different forms of occupation. The surface area and proportion allow generous corners as a support that facilitates the appropriation of space.
The structure is mainly determined by setting 3,60m short spans, matching the matrix of rooms. Therefore, multiple supports uphold CLT slabs: cross-laminated timber bearing walls in the façade and a system of laminated timber columns and beams in the centred bays. The structure is optimised by compensating momentums with multiple supports and cantilevers at all ends.
In order to achieve economic feasibility in social housing, timber volume needed by built squared metre is been optimised down to 0,24m3/m2
The façade’s construction system and the structure joints are both solved by mechanical bonds, avoiding the use of scaffolds. The exterior building skin is built up with electro welded wire mesh, holding/bearing sun shading and filtering sights. By bending, this element improve steadiness and at the same time it shapes the terrace’s handrail.

 © José Hevia
© José Hevia
 © José Hevia
© José Hevia
 © José Hevia
© José Hevia
 © José Hevia
© José Hevia
 © José Hevia
© José Hevia