Kindergarten and School Extension
Site
The location is characterised by remarkably flat terrain, noticeable several meters high pines and close presence of workers neighbourhood Kidricevo, designed on the principles of modernistic urban planning (urban plan set by architect Ravnikar, architecture made by Fuerst; both were Plecniks students).
Despite the exceptional urban placement of 20 elongated blocks of flats with their outstanding relation of built structure and surrounding greenery, the settlement not only lacked a kindergarten but also public open spaces or any other identity centers.
The new building reads topographic characteristics of the location and at the same time takes into consideration aforementioned needs of the neighboring community. The positioning of buildings masses creates several sequences of public and half-public spaces, visually interconnected through a range of transparent surfaces. As a result, it introduces new public places and activity areas to the settlement.
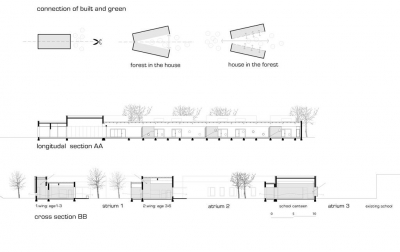
Concept
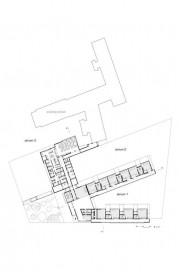
The architectural concept emerges from the idea of exchanging and interconnecting built and green spaces, creating various views and allowing constant contact with nature. The plan of building composed of three elongated volumes (relating to the elongated buildings in neighbourhood) separated by functionally divided courtyards. Two differently designed wings occupied by groups of children aged1-3 (three units) and those aged 3-6 (six units) are connected through transparent, multifunctional activity space. The third wing, consisting of administration, kitchen and school canteen geometrically and functionally refers to the existing school.
Interior
The composition of this single storey building with green atriums and precisely positioned glass surfaces enables a variety of views between classrooms, activity areas, corridors, outdoor spaces, canteen and school. The interior of the object surprises with particularly bright spaces, height variations, light effects and clever solutions of use of mixed spaces. Classrooms connect through wide doors, childrens slides and wall domes to bright corridors, which function as an extension of playing area. Childrens lavatories with their center element for playing - water fountains - allow children from two classes to socialize.
A foldable wall between the gym and central cloakroom offers possibility to connect them into a small hall for events.
Outdoor space
The entrance to the building is marked by concrete entrance platform, which provides a new public square for the municipality Round elements made out of different materials grass, sand, wood and foam - placed on this square invite visitors to touch them.
Construction system, materials
The building has skeleton concrete construction with brick fillings, flat roof based on steel plates covered with layers of insulation and greenery. Doors and windows are wooden; façade is made out of cement composite panels divided by wooden battens. Floors are covered with PE acoustic gum, except for the classrooms where parquet was used.
Sustainability
Kindergarten as a public building needs to minimize the costs of maintenance. To reduce the heat loss, a system of forced ventilation with heat recuperation (injection of fresh air heated by the exhausted air) has been installed. The green flat roof is covered with sun cells for heating of water. Children s units have floor heating providing pleasant touch for playing and crawling.







.jpg)